
Laser Flexibility
Up to five internal lasers and additional external laser ports for a range of lasers

Send us your samples, and we can measure them live in an online demonstration
Contact us to arrange an online demonstration

Laser Flexibility

Multi-detector

Dual Spectrograph

Raman and Beyond

Future Proof

Truly Confocal
"*" indicates required fields
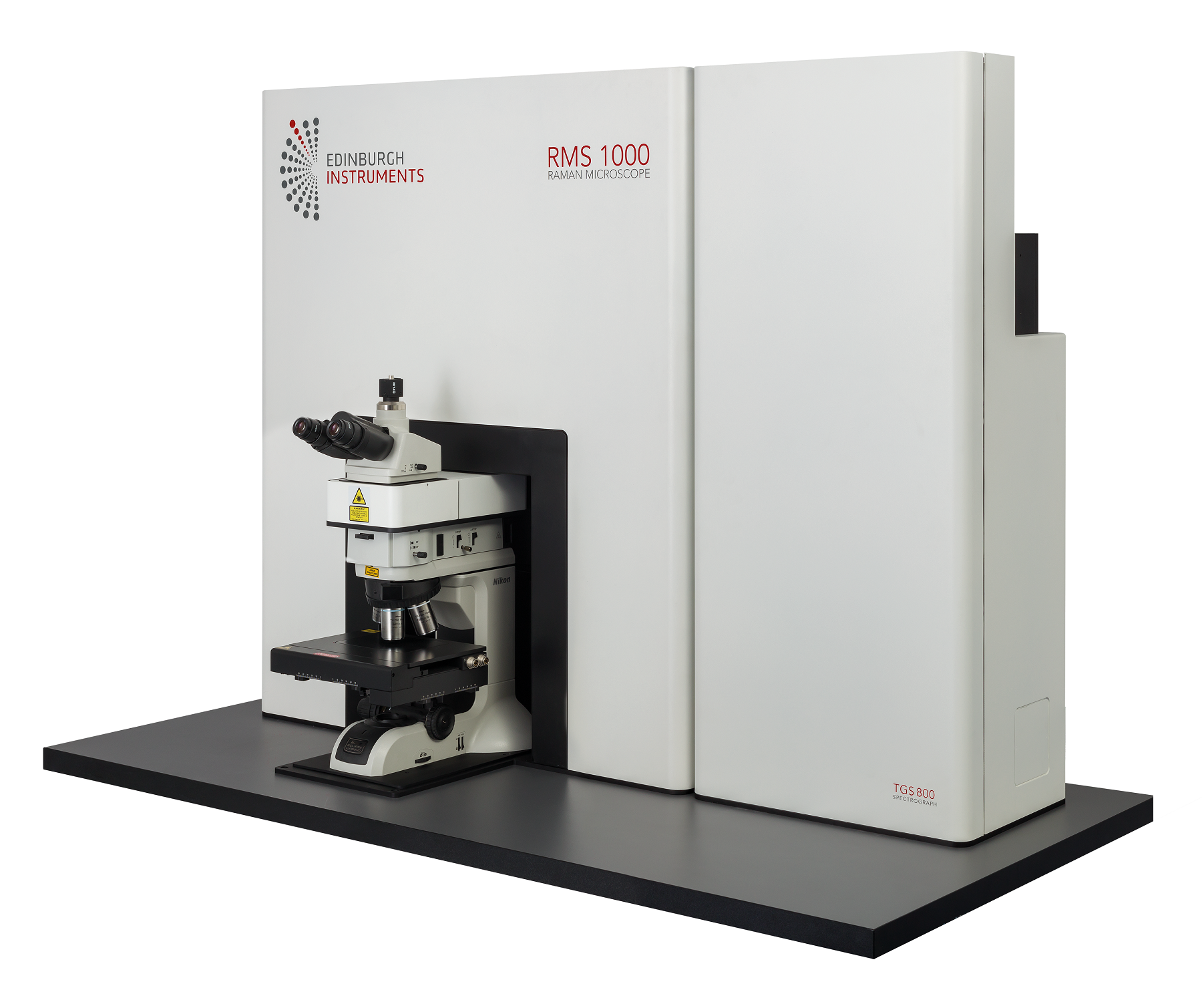
The RMS1000 is a Multimodal Confocal Raman Microscope built for adaptability and designed to grow, upgrade, and evolve with your research needs.
Built without compromise, this premium research tool offers unmatched specifications and ease of use. Its unique design allows full optimisation to any Raman microscopy application. With versatile laser, detector, and spectrograph options, the RMS1000 is perfect for any laboratory, finding applications in bioscience, nanomaterials, pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, geology, and more.
The RMS1000 is more than a Raman-only system. Harnessing Edinburgh Instruments’ extensive expertise in photoluminescence, we’ve integrated advanced fluorescence techniques to create a user-friendly, multimodal instrument. Seamlessly operate Raman and fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM) in a single software package, making RaFLIM® data acquisition from the same point both easy and intuitive.
Expanding on Raman and FLIM, the RMS1000 is exceptionally versatile, expandable to integrate a multitude of advanced techniques. Unlock precise imaging across various techniques with our multimodal system, featuring Raman, photoluminescence (PL), fluorescence life time imaging (FLIM), phosphorescence lifetime imaging (PLIM), multiphoton techniques, and antibunching capabilities.
The RMS1000 is a cutting-edge Multimodal Confocal Raman Microscope renowned for its adaptability and ease of upgrade. Its open architecture design facilitates seamless upgrades without compromising the high specifications of the core instrument. Built to adapt to your research needs, it integrates advanced techniques ensuring precise and comprehensive imaging capabilities across various scientific disciplines.
Ramacle® is an all-encompassing software package written for complete instrument control and data handling for all multimodal techniques on the RMS1000.
Just like the hardware, the software operating the RMS1000 adapts to your research need. Ramacle controls all RMS1000 functions with a straightforward design concept. It focuses on all modern Raman spectroscopy applications, and beyond. For example, running Raman and FLIM maps easily in one comprehensive platform.
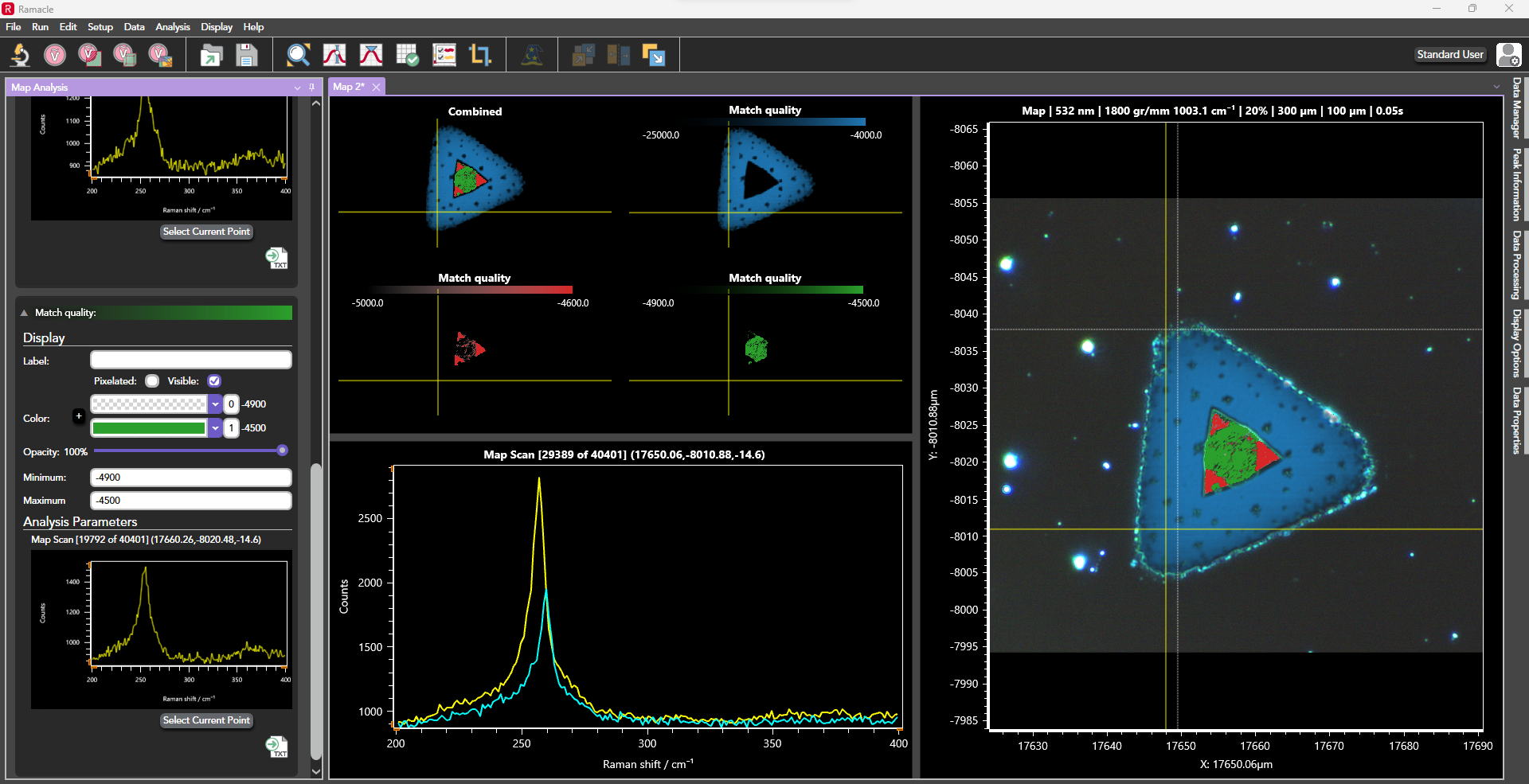
Figure 1: Ramacle software interface
With Ramacle, you can easily navigates from microscope set up to measurement set up and offers computer-controlled measurement conditions such as laser excitation, grating, pinhole size etc. On the RMS1000, Ramacle comes with standard data acquisition methods such as single measurements, multiple and accumulated scans, kinetic scan, as well as a comprehensive suite of mapping techniques e.g. 2D, 3D, SurfMAP, and FastMAP. Upgrades and accessories such as temperature stages and multiwell plates unlock additional software features.
2D mapping and 3D mapping allow the user to see distribution of components, as well as revealing areas under high stress or strain, and defects. If using short exposure times FastMAP® is also available to reduce total acquisition times.
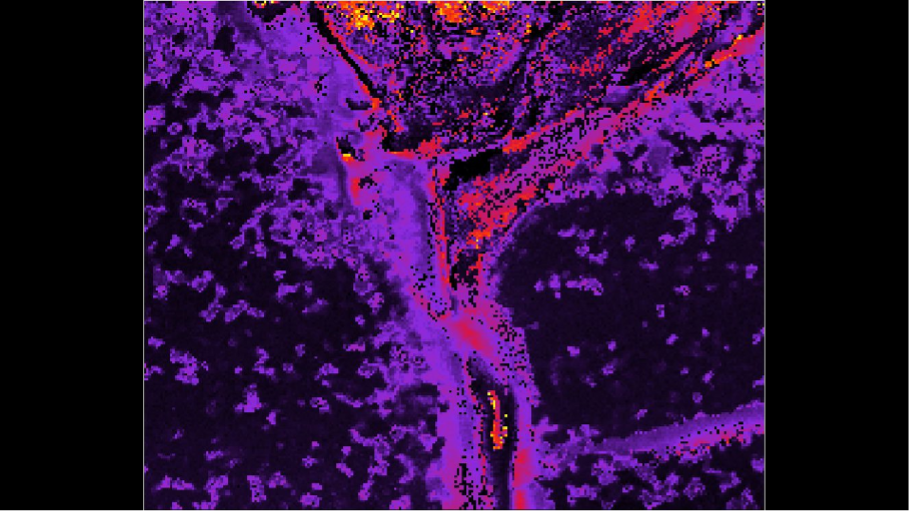
Figure 1: 2D Raman mapping showing nanocrystalline silicon and strain (pink, yellow, red) in a defective wafer
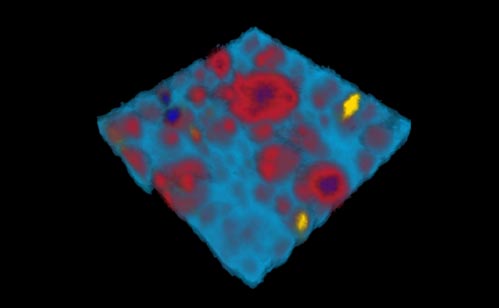
Figure 2: 3D Raman map of a pharmaceutical oil-in-water emulsion with TiO2 inclusions
SurfMAP® is a tool which allows accurate mapping of uneven surfaces giving the user assurance that their measurements are in focus and data is reliable. Ramacle builds a surface image which can be viewed in 2D and in 3D topography view. The software then acquires the spectral map moving the stage in X, Y, and Z for perfect laser focus.
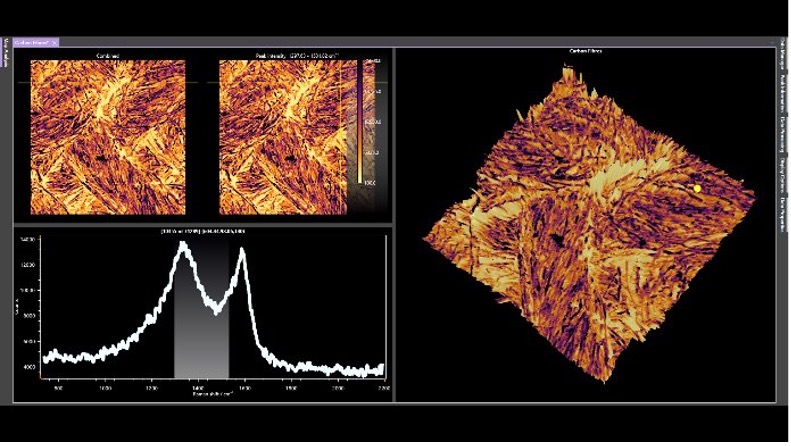
Figure 1: Raman SurfMAP® of carbon fibres tracking the D and G bands
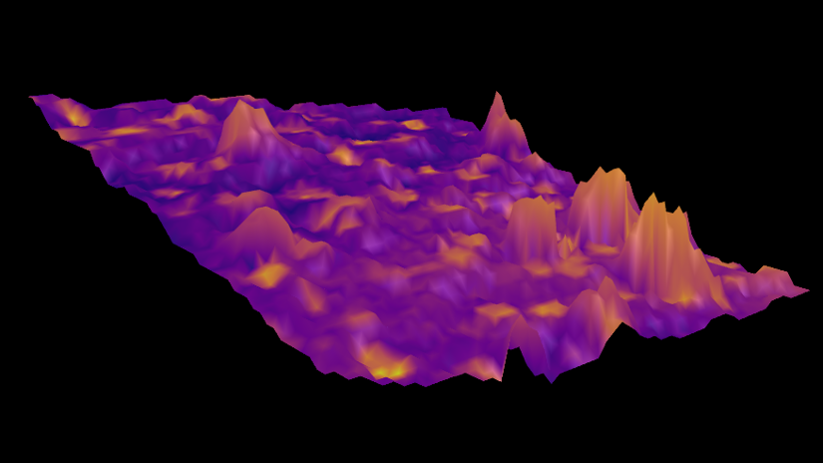
Figure 2: Raman SurfMap of an antipsychotic pharmaceutical drug
RaFLIM is a standout technique on the RMS1000. Combining Raman and FLIM to create maps of the same area, with the same spatial resolution (laser dependent). Operating measurement acquisition and data analysis in Ramacle for ease of use and continuity.
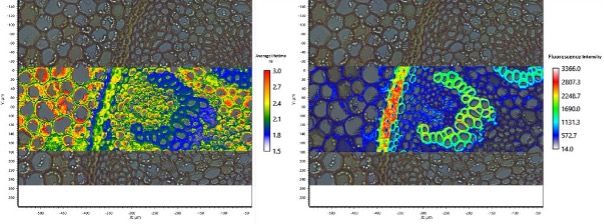
Figure 1: Average lifetime and fluorescence intensity image of a Convallaria Rhizome section stained with Acridine Orange. FLIM reveals variation in lifetime across lignified and pectin rich cell walls (2 exponential tail fitting).
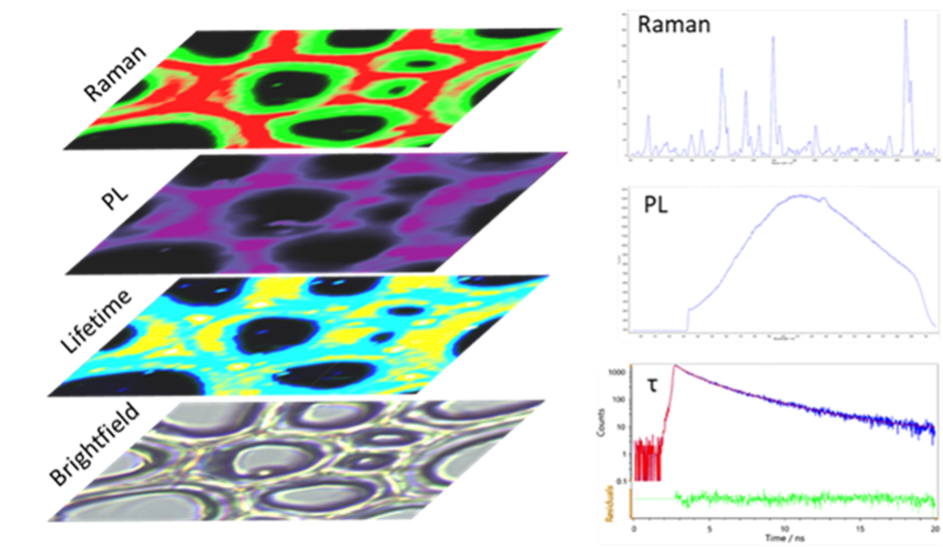
Figure 2: Biochemical analysis of woody plant cell walls using our multi-modal micro-spectroscopy approach.
The RMS1000’s external laser port unlocks limitless potential for advanced techniques like multiphoton imaging. Techniques such as two-photon excited fluorescence (2PEF) and second harmonic generation (SHG) are ideal for studying biological samples. Both 2PEF and SHG demand extremely high excitation intensity, provided by a mode-locked femtosecond pulsed laser.
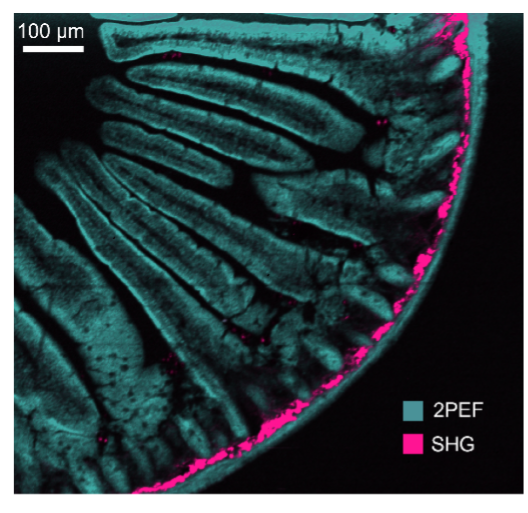
Figure 1: Mouse intestine stained with Alexa Fluor® 568
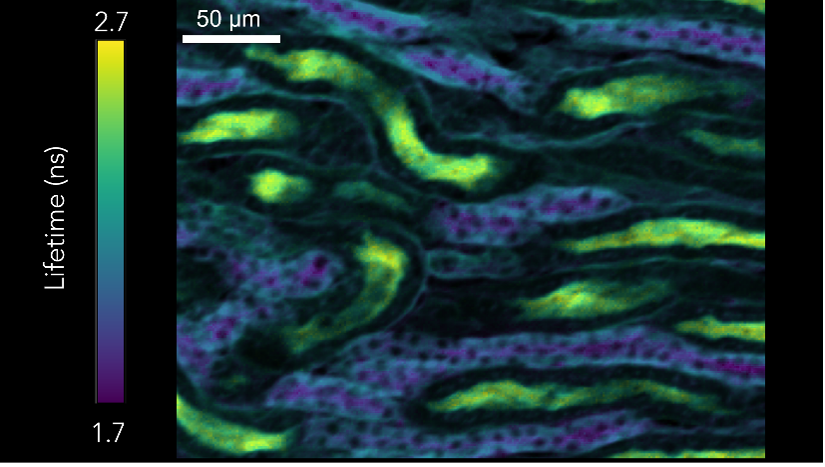
Figure 2: Photon lifetime imaging of mouse kidney sample
The sample of the mouse intestine (Figure 1) stained with Alexa Fluor® 568. Simultaneous measuring of spectral 2PEF and SHG from Alexa Fluor® 568 dye and fibrillar collagen respectively. Measurement using femtosecond laser and CCD camera. Using the same laser, two photon lifetime imaging was carried out an a sample of mouse kidney (Figure 2). This time a Hybrid Photodetector was used with TCSPC.
2D materials are also often studied with different measurement techniques, the RMS1000 can easily be configured to carry out all imaging techniques on the same sample area providing a full suite of complimentary information. Raman and PL images were collected using a 532 nm laser, whilst the SHG was acquired using a femtosecond laser.
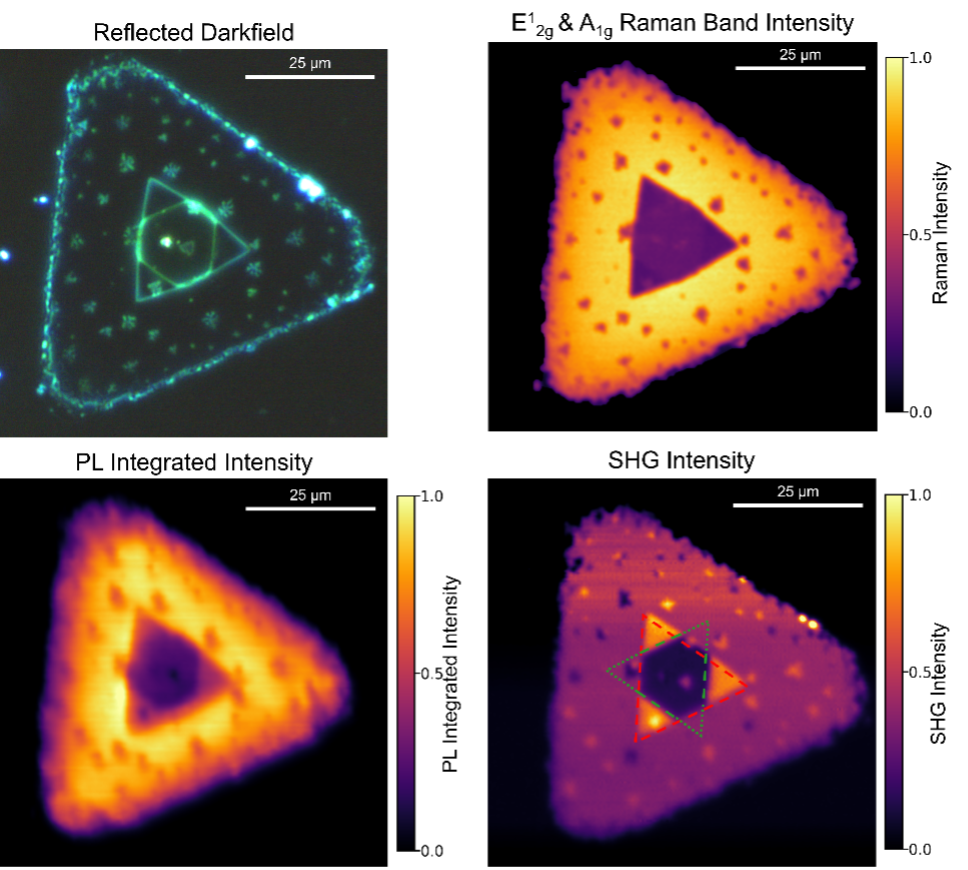
Figure 3: Sample of WSe2 crystal. The darkfield (DF) image reveals areas of different heights. Raman, PL, and SHG images can be used correlatively to identify layer number, and highlight areas of stress, strain, dopants, and defects
The RMS1000 is built with flexibility in mind. A choice of excitation lasers (internal or external to the system) and associated laser rejection filters (both edge and notch) are available. Additionally pulsed diode lasers such as our EPL series can be added if fluorescence lifetime measurements are required.

The RMS1000 can be fitted with both standard and long focal length spectrographs. This allows the system to be configured for ultimate spectral resolution, maximum optical throughput, low wavelength and ultraviolet spectral ranges, or for highly sensitive measurements.

The RMS1000 uses either an upright or inverted microscope platform which is compatible with all standard microscopy applications.
Brightfield, darkfield, polarised light, differential interference contrast (DIC) and fluorescence accessories are all available. A large choice of high-quality microscope objectives, high-performance visualisation cameras, collimators and illuminators can be added to the microscope at any time.

Manual or motorised stages are available. The motorised stage allows automated XYZ Raman and fluorescence maps to be obtained and generated through Ramacle. Additional sample stages are compatible with theRMS1000, such as temperature stages, electrochemical cells, and diamond anvil cells.

Other accessories such as a polarisation kit, cuvette holder, and a Class I laser safety enclosure are also available to further expand the capabilities, flexibility and safety of your RMS1000 system. Coupling to other fluorescence spectrometers is also possible.

| Specifications | ||
|---|---|---|
| LASERS | Up to 5 integrated narrow-band lasers: 532 nm, 638 nm, 785 nm typically used | |
| Additional lasers from UV to NIR are available. External lasers can be integrated | ||
| Laser selection is fully computer-controlled | ||
| Associated laser rejection filters included, fully computer-controlled | ||
| SPECTROGRAPHS | Wavelength Range | 200 nm - 2,200 nm |
| Gratings | 5-position grating turrets | |
| Slits | Continuously adjustable, fully computer-controlled | |
| SPECTRAL RESOLUTION | From <0.1 cm-1 (depending on grating, laser and CCD selection) | |
| SPATIAL RESOLUTION | XY (lateral), Z (axial) | 0.25 µm, <1 µm (depending on laser and microscope objective) |
| SPECTRAL RANGE | 5 cm-1 * - 30,000 cm-1 (* with low wavenumber attachment) | |
| CONFOCAL IMAGING | Adjustable confocal pinhole, fully computer-controlled | |
| DETECTORS | CCD Detector | High sensitivity ultra low noise spectroscopy CCDs |
| 1650 x 200 pixels, TE-cooled -60°C (standard) | ||
| 2000 x 256 pixels, TE-cooled -60°C (enhanced sensitivity / spectral range) | ||
| Optional Second Detector | EMCCD detector, 1600 x 200 pixels, TE-cooled -100°C (fast response time) | |
| InGaAs array, 1024 pixel, TE-cooled -90°C, up to 2,200 nm | ||
| SOFTWARE | Ramacle® | Comprehensive all-in-one, intuitive software package |
| Optional | Chemometric, spectral library packages | |
| FLUORESCENCE | Spectral | With low resolution grating and integrated CCD |
| Lifetime | With picosecond pulsed lasers, TCSPC electronics, fast photon counting detectors | |
| Spectral and lifetime fluorescence mapping is also available | ||
| LASER SAFETY | Without Laser Enclosure | Class 3B (depending on external laser source) |
| With Laser Enclosure | Class 1 | |
| DIMENSIONS | W x D x H | From 975 mm x 610 mm x 1170 mm |
| Weight | From 114 kg |